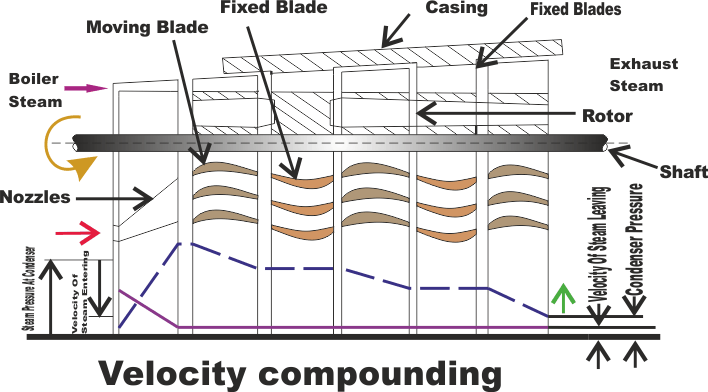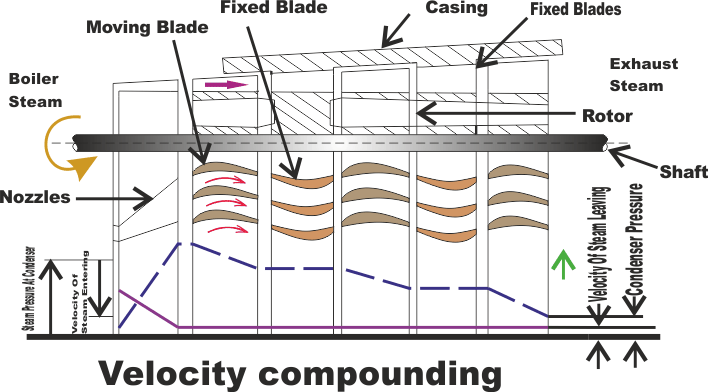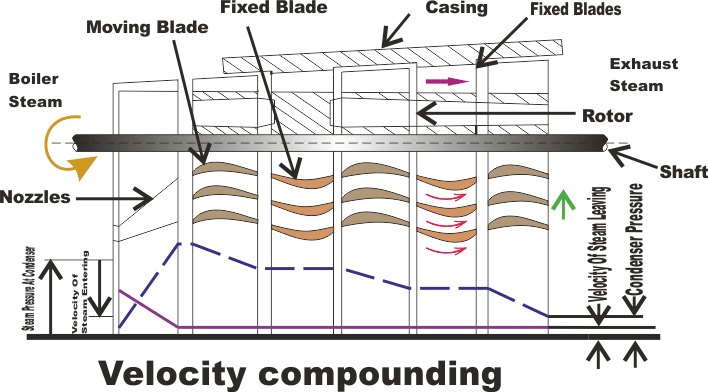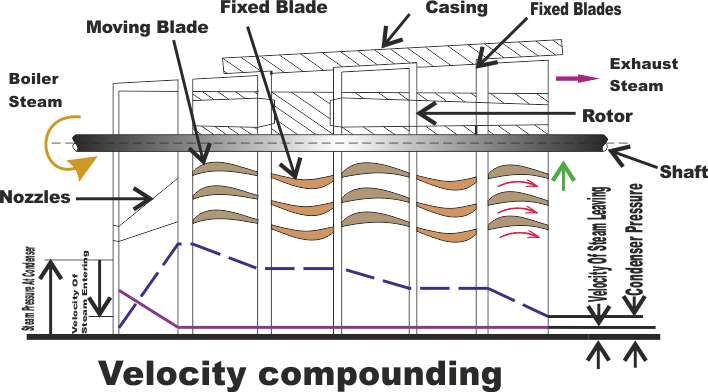
In this method, there are number of moving blades (M.B), separated by rings of fixed blades (G.B) , Keyed in series on a common shaft. The stem from the boiler is passed through the row of Nozzles from the boiler pressure to condenser pressure and attains high velocity.
The high velocity steam jet passes over the rings of moving blades and fixed blades alternatively. During which, a part of kinetic energy is absorbed in each ring of moving blades. The direction of steam is changed without altering much its velocity in the rings of fixed blades. Thus, all the Kinetic energy is utilized in moving blades. Since there is no pressure drop as the steam passes over the moving blades, the turbine is thus of impulse type.
The pressure drops fully at the nozzle itself and the pressure is kept remains constant in moving blades and fixed blades. The velocity of the steam coming out of nozzle is very high and it is reduced in stage - by - stage of moving blades. Hence, it is known as velocity compounding. The velocity of steam is constant while passing through fixed blades.
Example of this type of turbine is low. A three rows wheel is used for driving small machines. It may be noted that a two rows wheel is more efficient than the three row wheel turbines.
Advantages :
* Its Initial cost is less because of few number of stages.
* Less space is required.
* The System is reliable and easy to start.
* There is need of strong casing due to low pressure.
Disadvantages :
* Frictional losses are high due to high initial velocity. Hence, the efficiency is low.
* The ratio of blade velocity to steam velocity is not optimum for all wheels. It also reduces the efficiency.
* The Power developed in later rows is only a fraction of the power developed in the first row. But, the space requirement of all the stages is still the same. This increases the cost and material requirement.
Comments
Post a Comment