A Solid is an ordered cluster of molecules. All solids are either amorphous or crystalline. Solids in which the atoms are arranged chaotically, without any vestige of order, are amorphous. Examples are : plastics, glass, etc. On the contrary, solids in which the atoms arrange themselves in a definite or orderly manner and form are called crystalline which include all metals. Solid are classified according to the type of bond which holds the constituent particles of the solid together. On this basis solids can be classifieds as (1) ionic , (2) molecular , (3) Covalent , (4) Metallic.
IONIC SOLIDS :
An Ionic crystal is held together by ionic bond. Ionic solids have generally high melting points. This is due to the reason that considerable thermal energy is needed to overcome the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Ionic substances also carry electric currents in the molten states as the free ions move in electric potential difference. Particles of unit cells are anions and cations.
MOLECULAR SOLIDS :
Molecular Solids are often known as Vandewall's solids have molecules as individual units while the bonds within the molecules are covalent, the forces of attraction between the molecules are quite weak. Because of the relatively weak intermolecular force of attraction, molecular solids are soft, have low melting and boiling points and high vapor pressure.
COVALENT SOLIDS :
In Covalent Solids, atoms are held to one another by covalent linkage forming a giant network. Diamond, Si C, SiO2 are the examples because of their strongly bonded rigid structures, most covalent solids are very hard and melt at high temperatures.
METALLIC SOLIDS :
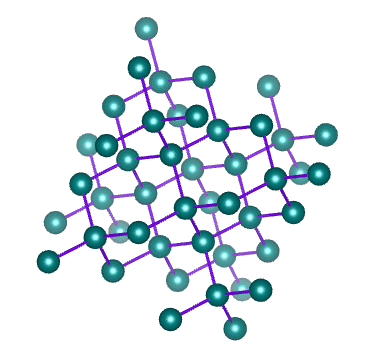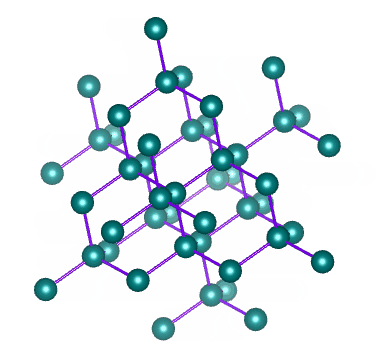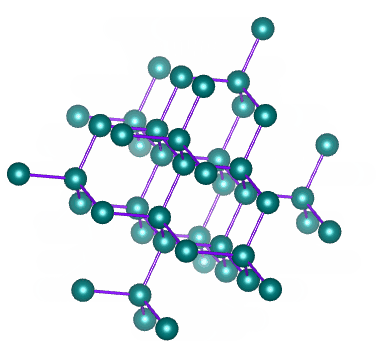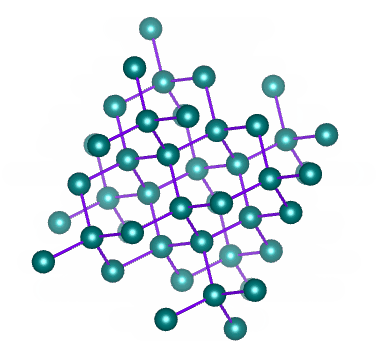
Metallic Solids are those in which positive ions occupy the lattice sites. The atoms of a metal assume nearly fixed positions relative to each other. A solid metal usually composed of a multitude of crystals. Within any one crystal, the atomic arrangement is repeated by adjacent atoms. An Imaginary line can be drawn to the string of atoms arranged side by side. In fact, such lines can be drawn in three coordinate directions and form a lattice work. This definite and orderly manner and form of the atoms producing a small, repeating, three dimensional, geometrical pattern having the same symmetry as the crystal in the aggregate is called the Space lattice or Crystal lattice.
The Space lattice of any solid is built up of innumerable conjugate cells inside of which the atoms are arranged in a definite order. Each of these cells is known as unit cell. The unit cells may be considered as the effective building blocks of which solid metal is built , much the same as bricks are the building blocks of which walls are built. Thus, the basic geometric body created upon changing from the liquid to the solid state is referred to as unit cell., and the aggregate (innumerable repetition of unit cells) is known as the space lattice.
There are altogether fourteen different crystal lattices, known as Bravais space lattices. In metals, however, there are six lattices.
These are ,
i) Body - centred cubic (bcc)
ii) Face centred cubic (FCC)
iii) Close packed hexagonal ( hcp)
iv) Cubic,
v) Body centred tetragonal and
vi) Rhombohedral.



Comments
Post a Comment