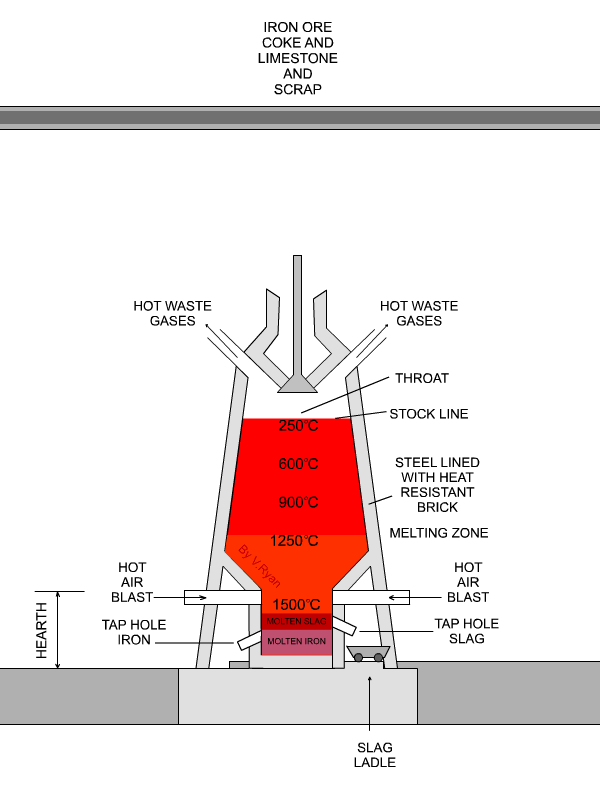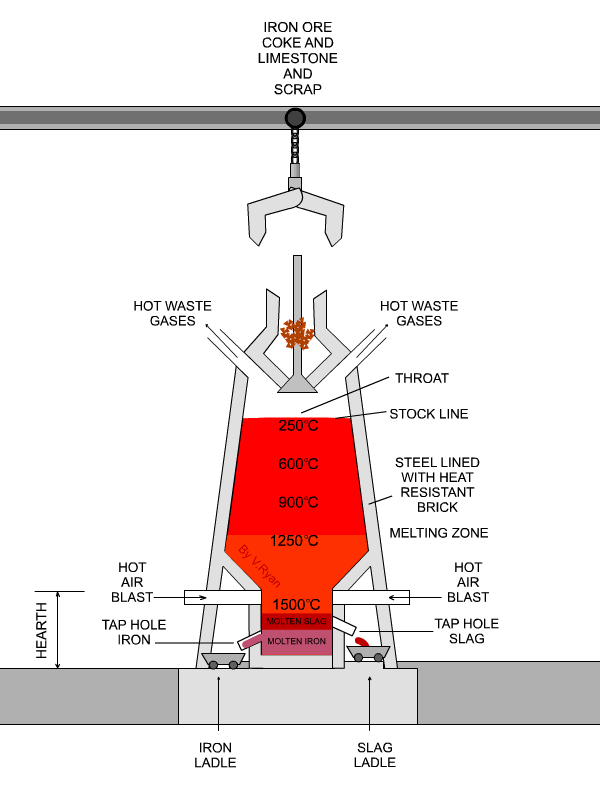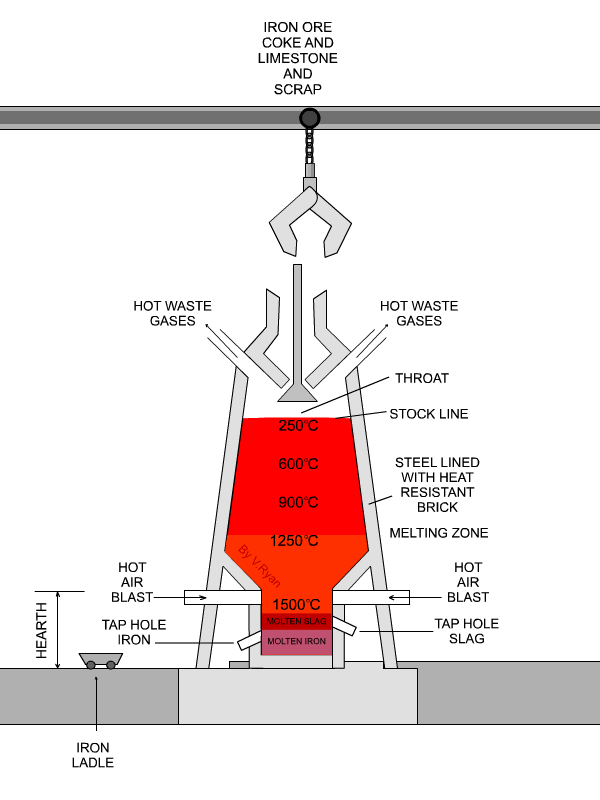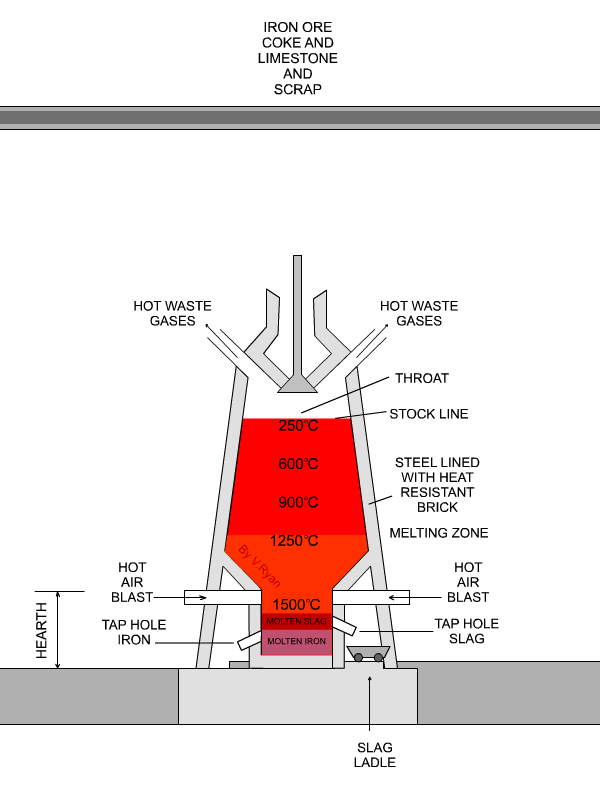
The Blast furnace is the vertical furnace designed for continuous operation. The smelting room of the blast furnace comprises a throat, stack, body, bosh and hearth.
The Raw materials (alternate layers of ore, coke , flux) , known as the charge, are taken to the top of the furnace by a specially designed bucket called "skip" running along an incline. The charge is then introduced into the throat of the furnace by means of a double bell and hopper arrangement to prevent the escape of blast furnace gas which is used as a fuel. The proportions of the raw materials are approximately one-half iron ore, one-third fuel, and one sixth flux. It may be pointed out , for instance to make 100 tons of pig iron it requires about 180 tons of iron ore, nearly 95 tons of coke, 50 tons of flux, and about 350 tons of preheated air blast. In addition to pig iron, about 60 tons of slag and 50 tons of gas are produced.
A hot blast is forced into the furnace through a number of nozzles called Tuyeres. The Tuyeres are cooled by water circulating between the pipe walls. The air blast is heated to minimize fuel consumption by passing the cold air blast through the heated checker-work of hot blast stoves.
The temperatures of the furnace just above the level of the Tuyeres (melting zone) being 1000*C to 1700*C all substances inside the furnace start melting in the heat. The limestone that serves as a flux is combined with the ore to form a molten slag which floats on the top of the molten iron. The slag is tapped off from the furnace through the slag hole. The molten iron is tapped at intervals from six to twelve hours through a tapping hole, the blast being turned of mean while. The furnace is kept in operation until it gets worn out.
According to the type of the plant the molten iron may be used in one or more of the following ways.
1. Cast in Pig Bed.
2. Cast in Pig-Casting Machine.
3. Transferred in hot metal ladles direct to an adjacent steel - making process.
Pig beds are sand molds in the form a grid prepared in the ground along side the furnace . The bars (pigs) cast in this way are about 1m long with a D- shaped cross section measuring about 100mm each way. The modern method of casting pig iron which has largely superseded the older pig-bed method is to employ a pig casting machine. This consists of a series of hematite iron or steel molds, each about 600 mm * 200 mm * 90mm, fixed to an endless chain conveyor , the assembly being mounted on a suitable construction arranged on a slight slope.
While the Iron is in the furnace it picks up 3 to 4 percent of carbon and a small amount of Sulphur from the coke. The silicon, manganese and phosphorus as well as most of the Sulphur in the pig iron are derived from the ore. The high amount of the carbon makes the pig iron very hard and brittle and unsuitable for making any useful article. Pig iron, is therefore refined and re-melted to produce other varieties of iron and steel.
Comments
Post a Comment